|
Introduction Before we start on Blockchain, let me dispel the biggest misconception out there. Blockchain is not spelled “ B I T C O I N”. There are several parallels between blockchain and the internet of the 90’s. You can call blockchain as the foundation of a new internet. As I have already hinted, most people think of blockchain as Bitcoin, this is akin to saying internet is email. Just as email is one of the use-cases of internet, Bitcoin a cryptocurrency, is one of its numerous use-cases. Bitcoin makes money transfer inexpensive, seamless and instantaneous across borders. You may ask what is wrong with the internet, why repair what is not broken? Internet was supposed to solve a few problems for us communication, information, distribution, trust and disintermediation. Internet solved all of these issues except trust and disintermediation. We cannot rely on the information on the internet and neither was it able to disintermediate everything. Actually, internet centralized power in certain big corporations Facebook, Google, Amazon etc. Blockchain aims to solve the trust and disintermediation issues. What is Blockchain? As a finance professional, you know every transaction in the world has to be recorded in a ledger somewhere. If I bought a Mac with my credit card, it is recorded in my credit card ledger, the Applestore’s ledger and also in Apple’s ledger. These are recorded separately and need to be reconciled. In some real-world transactions there are more than 10 parties involved and the reconciliation is messy, expensive, inefficient and vulnerable. What if this whole transaction and asset registry is recorded in one distributed ledger, which is verified by all business participants, who have vested interest in keeping the information accurate, is immutable and has impregnable security. You have chanced upon blockchain, the “single source of truth”,. In accounting terms, blockchain is one giant decentralized distributed immutable accounting system. The blockchain is not stored in the cloud but in several peoples computers, think of the P2P music sharing service, Napster of the late 90’s. If one does a journal entry, it has to be verified and approved by a majority of the people participating in the blockchain. Once verified, it cannot be altered. Now, the next journal entry is immutably linked to the previous journal entry so on and so forth in a chronological order. Each journal entry can be called a block and all the journal entries collectively is called blockchain. To give another analogy, think of excel and its various problems. Excel is the old way of doing things, with different versions of the same file floating across the network or in emails. If you have graduated to Google Sheets then you are using a single version and hence it is highly reliable. To hack a blockchain, the hacker has to compromise more than 50% of the globally distributed participants and do so faster than new blocks are created. This means blockchain cannot be corrupted, erased or hacked. Blockchains can be private, public or hybrid to limit access. Private data such as a patient’s medical records can be encrypted and can only be decoded with a patient’s private key. Why go through this pain of creating such a system? There is a lot of friction when you have to make entries in different ledgers. Friction adds costs and time delays while at the same time not adding any reliability. Blockchain reduces costs while making the system reliable and trustworthy. What are its uses ? There are numerous uses, below are just a handful.
Conclusion A January 2017 World Economic Forum report predicted that by 2025 10 percent of global GDP will be stored on blockchains or blockchain-related technology. Every company is using blockchain right now from Google, Microsoft, IBM, Walmart, Chase just to name a few. In fact Bank of America, Mastercard, Fidelity and IBM are the top four blockchain patent owners. This is similar to the 90’s, either you adapt or perish. Blockchain companies will disrupt companies that were disruptors in the internet age and it will happen much faster.
0 Comments
I have created budgets for a lot of SaaS and non-SaaS startups and am sharing the budget template. If the company is mature enough you will need to use a system like Adaptive or Hyperion. However, the below google template can be used as a good starting point to create your budget for most of the startups. Please feel free to copy, modify and use.
Link to the Master SaaS budgeting spreadsheet I created a SaaS pricing deck for one of my entrepreneur friends a while back. Updated it with changes and putting it here. The biggest cost of Product and Engineering, other than Headcount is usually the AWS hosting charges. I am jotting down my understanding of AWS hosting charges from a finance perspective.
AWS offers around 70 services but the primary cost is mostly associated with Simple Storage (S3) and Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2). AWS pricing is similar to the utility bill. You pay for what you consume and can disconnect anytime. There is however, a twist. The utility bill has a step-up function i.e. if you exceed a certain usage your pricing goes up. AWS has a step-down function i.e. if you exceed a certain usage your pricing goes down. Let’s talk about the two main headers, S3 and EC2. Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) Cloud Storage pricing is here . S3 consists of the following major headers. Storage Pricing There are three different tiers for Storage; Standard Storage, Standard - Infrequent Access Storage and Glacier Storage. Standard storage is used for your production data that is frequently accessed. This is the most expensive of the storage tiers. Strategically place it in different regions for better accessibility. Standard - Infrequent Access Storage is as the name suggests for infrequently accessed data. This is cheaper than Standard Storage but has higher charges for data transfer. Glacier Storage is cold storage to store data for regulatory or compliance purposes. Data can be retrieved if needed to the other two tiers for accessibility. Request Pricing (Accessing Data from Storage) There are different pricing ranges for accessing data from the above storage types. Data Transfer Data transfers into S3 and to EC2 in the same region is 0 but transfers from S3 to internet and to EC2 in a different region costs you. Amazon S3 Transfer Acceleration S3 Transfer Acceleration is used if you need faster “Data transfer” (see above). AWS checks if it can move the data faster than “Data Transfer” and will charge extra only for accelerated data transfer. AWS GovCloud Region GovCloud is for Government agencies and contractors for compliance and regulatory purposes. Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) EC2 pricing Is here. EC2 is a virtual server for running applications on the AWS server. Think about it as memory needed to run the applications. There are 4 types of EC2 instances sorted from cheapest to the most expensive; Dedicated Hosts, Reserved instances, Spot instances and On-demand instances. Every time you use EC2 you will need EBS. EBS is like a virtual hard drive attached to your EC2 instance. It is so as to segregate compute from your data storage. EBS pricing is here There are other small charges other than EC2 and S3 but mostly minimal. With this understanding an FP&A professional can intelligently forecast the AWS hosting charges with inputs from Product and Engineering. In wandering around the Internet as I follow interesting companies, I noticed some action with AppDynamics. AppDynamics is an intelligent application performance monitoring company. Check more here. Their total funding as of date is 350M+. More details here. They just filed an S-1 on December 28th, 2016. See here.
The company highlights are as follows:
This Raises Some Questions and Thoughts The cash flow from operations (CFO) for the 9 months ending Oct 31 2016 was only negative 2.2M USD. Can that be improved? CFO in the last quarter of 2016( Oct 31 2015 - Jan 31 2016) was 7M+. Is the company approaching positive cash flows? How much of the current $12B TAM can AppDynamics capture? There is already plenty of competition including New Relic, which went public a couple of years back. They aren’t profitable either. The Sales & Marketing (S&M) spend seems high. S&M spend is $118M for 9 months ending Oct 31st 2016 while Revenue increased only 56M during the period over the corresponding 9 months in 2015. Is this just “landing” in the “land and expand” strategy? The S-1 takes this concern head on by stating: “ Investments we make in our sales capacity will occur in advance of any return on such investments, making it difficult for us to determine if we are efficiently allocating our resources in these areas”. New Relic ended the first half of the year with 122M in revenue whereas AppDynamics finished the last 9 months with 158M in revenue. New Relic as of Jan 6th had 1.6B in market cap and had been as high as 2B a few months back. What should AppDynamics valuation be? It last raised capital at 1.9B valuation. To sum it up, this will be a closely watched IPO in the tech industry, especially after a lackluster 2016. Anything that can be measured is a metric. KPI’s or Key performance indicators, are a subset of metrics and are, as the name suggests, key indicators of performance.KPI's should be religiously and objectively tracked. One should put a quarterly, yearly and multi-year target on the KPIs.
Each department or sub-departments can have their own KPI’s. However, at the executive level there should be a maximum of 5 KPI’s. Departmental KPI’s should be understood in the context of the executive KPIs. Executive KPI’s should be tightly aligned with company’s goals and strategy. KPI’s should be easily understood across the company so everyone is aware of the progress and the effort needed to get to the promised land and beyond. KPIs should be used in the forecast process so we can keep a close tab. KPI’s can also be used a compensation tool so the incentives are properly aligned. What is a cap table ?
Simply put, a cap table is a point in time ownership report. A cap table captures all transactions / option and warrant grants since the beginning of the company. A company’s capital structure (excluding debt) usually consists of preferred shares, common shares, warrants and options. Preferred shares are reserved for investors. Depending on the number of rounds Preferred shares are divided into different classes Preferred A, Preferred B, Preferred C and so on. Warrants are usually given to investors (mostly debt) to be converted into one of the Preferred share classes. Common Shares are also divided into classes let's just call it Common A and Common B, one of which is reserved for founders. The other class of Common Shares are for option conversion. Options are common stock options granted to employees (ISO’s) and consultants(NSO’s). If the value of options granted to an employee is greater than a $100K, then those options will be classified as NSO’s. The company’s outside counsel is usually responsible for managing the cap table. Software such as Solium or eShares is used. What is the use of cap table ? The most common use is it gives you the ownership details. However, there are plenty of other uses Fund Raising Most investors ask for Cap table along with an investor deck. This gives investors an idea of the capital structure and how they can fit in. On the other hand, it gives the founders an idea of how the capital structure will look if they raise a certain amount. Franchise Taxes Most companies register themselves in Delaware to save on corporate taxes. Companies, however, have to pay franchise taxes in Delaware. These taxes are calculated based on authorized shares. See here 409(a) valuation Companies issue stock options to its employees at board meeting every quarter. The stock options are valued by a valuation firm in a 409(a) report.(see my previous post on Option valuation). Companies are required to do a 409(a) valuation every year. Stock compensation Stock options are compensation similar to salary. Per US GAAP (ASC 718, previously FAS 123R), the company is required to record stock compensation in the financials. This requires an up to-date cap table. Softwares such as Solium or eShares can calculate it for you. Warrants are also compensation or contra-debt and need to be valued every year. IRS filings (Form 3921) Companies are required to report all stock option exercises with the IRS(Form 3921). See here . Softwares such as Solium or eShares can file it for you electronically. All you need to get TCC from IRS. First and last rule of choosing a system in this cloud era, never choose a client-server system. Here are some of the business system recommendations for a startup:
M&A Integration Success = Lesser Execution Risk = Financial success When to start M&A Integration ? M&A Integration planning should start very early in the M&A process, preferably at the deal screening stage. M&A Integration or the ease of it should be a big consideration on whether one goes ahead with the deal or not. By the close of the deal, an integration team should be established with clear integration strategies, steps, objectives and timeline. What constitutes M&A Integration ? Before I start, one-size-doesn’t fit all, so please modify accordingly. M&A integration constitutes integration of people, processes and systems(PPS), all of them in a reasonable time without impacting the M&A goals. All three of PPS are intertwined and equally important. People This is probably the most difficult of the integrations. Hence, this needs to start the earliest. Sometimes M&A involves companies from Europe or Asia, the culture and timezones are different. Your best employees are the most vulnerable and will be poached by competitors. So, clear, consistent and transparent communication from executives is the key. Here are some decision points that should be resolved quickly What does the org structure look like ? What is the integrated company culture ? What is the workforce strategy ? Processes “We have always done it this way”. You will hear this a lot. Document and understand the critical processes on both sides in each of the areas (Sales, finance, Engineering, operations etc.) and find a common ground. Rejig the processes to make them more efficient and effective. Systems Systems are the lifeline of the company. Disparate systems will give you misleading and wrong information. So, it is very important to have a single source of truth soon. Key systems should be understood for the combined company. Systems (and the underlying data) should be migrated seamlessly so as not to disrupt the current businesses. What constitutes a successful M&A integration ? A successful M&A integration is one in which the M&A thesis translates into intangible and tangible financial results. Before I start on the role of FP&A, let me add a little bit of history to the Finance organization. Traditionally, Controllers have risen to the CFO roles and the focus has primarily been on closing the books. Accounting typically looks at past events and is concerned with GAAP and tax compliance, FP&A on the other hand is concerned with future events with a good grasp of past events. Most business leaders see FP&A professional as someone, who comes out of the woodwork once a month and hammers them with a performance report. FP&A has been relegated to the role of creating budgets and providing reports but that is changing fast. FP&A personnel also need to work in changing the mindset of CEO’s and management. However, it still remains the prerogative of the CEO and CFO to decide FP&A’s role. FP&A cannot be thought of just financial instead it should is both financial and strategic. These are the overarching goals of an FP&A organization
These are some of the ongoing responsibilities of an FP&A organization. Creating Strategic Plans Let's start here. FP&A is responsible for creating budgets, long-range strategic plans and reporting. However, for most organizations the buck stops here and the rest is ignored. Business Partnership FP&A through its in-depth knowledge can work with business leaders and enable them to reach their short-term strategic and operational goals. Business Analysis FP&A should work seamlessly with the business, charting the risks and opportunities to shape the firm’s strategy A fully integrated FP&A is one in which every functional leader works with the FP&A organization in understanding repercussions of every major step. Please look at my previous post How to prepare the Budget / Operating Plan ? for creating Bottoms-up plan.
So what is top-down planning and why is it important ? Top-down planning is for creating the 3-5 year plan. It does not involve every functional leader but only a few select in the management. It is important so we can fund long-term expenditures and raise capital accordingly. What are the steps ?
As I embarked on my journey as a Head of Finance earlier this year, I envisioned it to be challenging. What I learned is something vastly different and very refreshing.
A typical CFO, I thought, is supposed to take care of only Accounting, FP&A, treasury, corporate development, taxes and compliance but to my pleasant surprise there is a completely different side to it. A CFO is now supposed to assume the COO, CCO, CIO, CPO, CDO and CSO roles on a consistent basis. Chief Operating Officer and Chief Collaboration Officer The CFO is now called upon to execute strategies set by the board/management team. That means collaborating across the organization and setting the big picture and goals for every department. The CFO is also now responsible for delivering results on a day-to-day basis. Chief Information Officer The CTO should focus more on the product and execution of the engineering team and not on the job as CIO. As the landscape moves to cloud, it is getting easier for the CFO to assume this role. The CFO should understand and integrate all the critical systems to facilitate a single source of truth. Chief Data Officer There is data everywhere especially with the advent of big data analytics. A CFO is supposed to simplify, convert and interpret data into real actionable insights. The CFO needs to understand and own not just financial but also sales, marketing, product and other operational KPIs. Chief People Officer Hiring and retaining talent has always been important. The CFO is now being constantly asked to talk to critical hires very early in the interview process for giving comfort. The CFO should also constantly keep the employees updated on the company’s plans and prospects. The CFO should also make sure that every department has enough bench strength to keep going in case of some unforeseen critical departures. Chief Strategy Officer A CFO need to the big contributor to the Sales and Product strategy. The CFO should also be able to marry finance, operational and external data(if any) into actionable strategy. One of my previous managers said “Operating plans become outdated as soon as we finalize it”. She was kidding but there is some truth to it. One cannot think of annual plans as static but as ‘ever-growing’ to address the changing market conditions, strategies and risks. The operating plan should be refreshed quarterly.
The steps need not be as comprehensive as preparing the annual plan but it nevertheless needs to reflect the changed circumstances. During your monthly/quarterly “budget versus actuals” meeting with the department heads, discuss how their department’s objectives and hence spending has changed. Incorporate those changes into the revised plan. Dont just throw away your old plan because it is a good tool to refine your next year’s plan. As we approach another year-end, I have been inundated with calls on how to prepare next year’s plan. Please note that guide below does not include everything so modify accordingly.
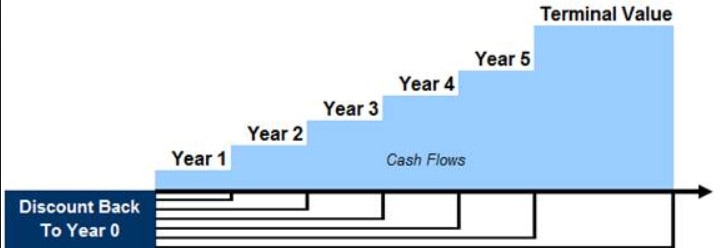
Here is the cheat-sheet Start with preparing the “best-guess budget” before you embark on the exercise. This seems counterintuitive but if you have been at the company you know the trends. If you are new get the actuals from accounting and do your best. This is so you can intelligently guide the department heads. Company Goals: Understand the company’s goals and how it translates into each department’s goals: The idea again is to have a simple overview of what the next year looks like. Set up a simple model. Budgeting for most departmental heads is a chore. Keeping the model simple is the key. Add actuals to the sheet too, so the departments have an idea. Divide the model into quarters instead of months. Send the model. Use a collaboration tool like Google Sheets to send each department head a sheet to enter a few days prior to your meeting. Here is a sample. Meet & Greet. Set up a meeting with department leaders: S&M, Product(R&D) and G&A Sales & Marketing: First and foremost comes the S&M leadership. The idea is to start from revenue and figure out how we will get there. What is needed in Headcount, Marketing and other spend to get to the projected Sales. For eg. How many MQL’s are needed to get to the sales number and what is the cost of getting those MQL’s. What do you need in Customer Success to support the growth in Customers ? Product : Second comes the Product department . Does the Product roadmap include everything that the sales need? What is needed in terms of Headcount, Software, hosting and others to achieve the Product roadmap. G&A: Armed with the S&M and R&D info, you will need to understand what is needed on the G&A side in terms of Headcount and other spend categories. Iterate: There will be plenty of iterations before everyone agrees. Every company/department is different and you need to navigate the waters accordingly. Bring it all together. Model everything to get a P&L, BS and Cash flow statement. There are number of tools like Adaptive Planning and Anaplan to capture all this. If you are a small company then you may want to start with excel. You will find that not one size fits all, so modify accordingly.  What is a 409(a) valuation ? For a private company, 409(a) valuation decides the value of stock options to be granted to your employees. Usually a DCF or backsolve valuation or a combination is done to get to the option price. I created a model to calculate option pricing using backsolve method. Please feel free to use it to validate your 409(a) valuation. With my compliments, you can follow my slideshow guide to create DCF valuation. Download Option Valuation Sheet Sometime back I trained a few academic folks on DCF valuation. Here is the presentation and an excel file with how to use DCF to calculate company value.
DCF Presentation Download DCF Valuation Sheet |











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed